How To Install Hping3 On Centos 6
Updated by LinodeWritten by Alex Fornuto
- How To Install Hping3 In Linux
- Centos 6 Install Ftp Server
- Centos 6 Install Php
- How To Install Hping3 On Centos 6
- Installing DKMS from the EPEL repository is recommended before installing VirtualBox. If you are not using a standard CentOS kernel, you must acquire and install.
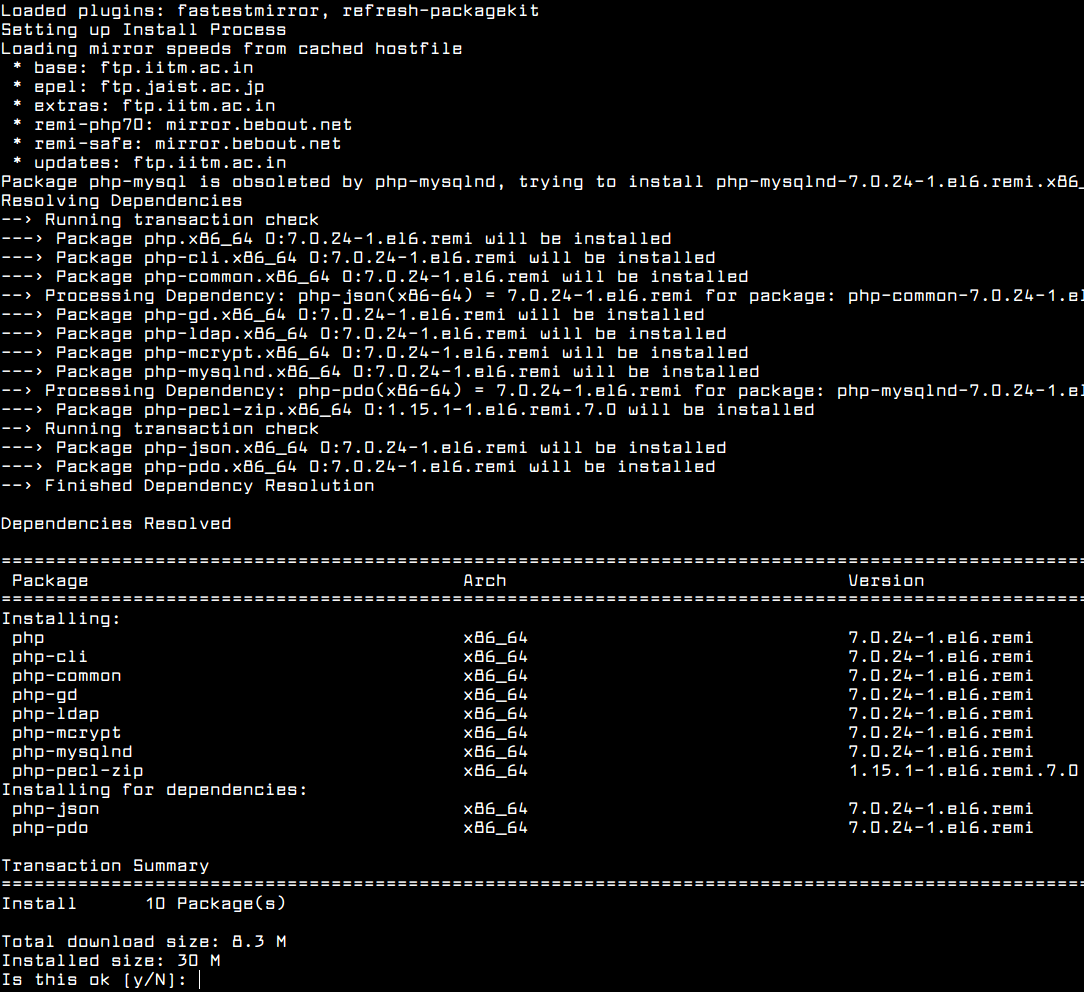
- LAMP stack is a group of open source software used to get web servers up and running. The acronym stands for Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP. Since the server is already running CentOS, the linux part is taken care of. Here is how to install the rest. The steps in this tutorial require the user on the.
H ow can I install Nginx web server On CentOS Linux 6 or Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 using yum command? Install Nginx Using Yum Command on CentOS/RHEL.
 Contribute on GitHub
Contribute on GitHubReport an Issue View File Edit File
MySQL is a popular database management system used for web and server applications. This guide will introduce how to install, configure and manage MySQL on a Linode running CentOS 6.
Notesudo. If you’re not familiar with the sudo command, you can check our Users and Groups guide.
Before You Begin
Ensure that you have followed the Getting Started and Securing Your Server guides, and the Linode’s hostname is set.
To check your hostname run:
The first command should show your short hostname, and the second should show your fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
Update your system:
Install and Start MySQL
How To Install Hping3 In Linux
Install MySQL and tell it which runlevels to start on:
Then to start the MySQL server:
MySQL will bind to localhost (127.0.0.1) by default. Please reference our MySQL remote access guide for information on connecting to your databases using SSH.
bind-address parameter in /etc/my.cnf. If you decide to bind MySQL to your public IP, you should implement firewall rules that only allow connections from specific IP addresses.Harden MySQL Server
Run the
mysql_secure_installationscript to address several security concerns in a default MySQL installation.
You will be given the choice to change the MySQL root password, remove anonymous user accounts, disable root logins outside of localhost, and remove test databases. It is recommended that you answer yes to these options. You can read more about the script in MySQL Reference Manual.
If you want to use PHP in conjunction with MySQL, you should install libapache2-mod-php and php-mysql sudo apt update && sudo apt install libapache2-mod-php php-mysql 2. The first command will update the package lists to ensure you get the latest version and dependencies for PHP. The second command will then download and install PHP. Installing apache and php. Sudo apt update && sudo apt install php Press y and ENTER when prompted to install the PHP package. Press y and ENTER when asked to continue.
Using MySQL
The standard tool for interacting with MySQL is the mysql client which installs with the mysql-server package. The MySQL client is used through a terminal.
Root Login
To log in to MySQL as the Root User:
When prompted, enter the root password you assigned when the mysql_secure_installation script was run.
You’ll then be presented with the MySQL monitor display:
To generate a list of commands for the MySQL prompt, enter
h. You’ll then see:
Create a New MySQL User and Database
In the example below,
testdbis the name of the database,testuseris the user, andpasswordis the user’s password.You can shorten this process by creating the user while assigning database permissions:
Then exit MySQL.
Create a Sample Table
Log back in as
testuser.Create a sample table called
customers. This creates a table with a customer ID field of the typeINTfor integer (auto-incremented for new records, used as the primary key), as well as two fields for storing the customer’s name.Then exit MySQL.
Reset the MySQL Root Password
If you forget your root MySQL password, it can be flushed and then reset.
Stop the current MySQL server instance, then restart it with an option to not ask for a password.
Reconnect to the MySQL server with the MySQL root account.
Use the following commands to reset root’s password. Replace
passwordwith a strong password.Then restart MySQL.
You’ll now be able to log in again using mysql -u root -p.
Tune MySQL
MySQL Tuner is a Perl script that connects to a running instance of MySQL and provides configuration recommendations based on workload. Ideally, the MySQL instance should have been operating for at least 24 hours before running the tuner. The longer the instance has been running, the better advice MySQL Tuner will give.
Download MySQL Tuner to your home directory.
To run it:
The output will show two areas of interest: General recommendations and Variables to adjust.
MySQL Tuner is an excellent starting point to optimize a MySQL server but it would be prudent to perform additional research for configurations tailored to the application(s) utilizing MySQL on your Linode.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
Centos 6 Install Ftp Server
Join our Community
Centos 6 Install Php
How To Install Hping3 On Centos 6
This guide is published under a CC BY-ND 4.0 license.
